Reciprocating seals/lip gaskets
Description
Types of lip gaskets
The following table shows types of gaskets for oil hydraulic cylinders and their characteristics.
Gaskets for oil hydraulic cylinders (dedicated to piston seals)
| Shape classification | Cross-section shape of gaskets | Material | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
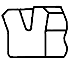
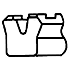
| U |
|
Urethane rubber, nitrile rubber, fluororubber | A gasket dedicated to piston seals. Gaskets made of urethane rubber have excellent wear resistance. When a notch is placed on the upper surface of the lip, relief performance is improved and thus a pressure accumulation phenomenon does not occur. | An asymmetrical U gasket. For low-temperature use, cold-resistant nitrile rubber gaskets should be used. Gaskets with a small cross-sectional area can be mounted in integrated grooves. |
|
||||
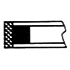
| S |
|
PTFE + (assembled) nitrile rubber | A gasket combining filled tetrafluoroethylene resin with a rubber ring. | Since the sliding surface is made of a self-lubricating material, sliding resistance is low and a stick slip phenomenon rarely occurs. Can be mounted in an integrated groove. |

|
PTFE + (assembled) nitrile rubber + (assembled) polyamide resin | A gasket combining filled tetrafluoroethylene resin and polyamide resin with a rubber ring. | A piston gasket with improved pressure resistance that can be mounted in an integrated groove. | |
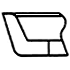
| L |
|
Urethane rubber, nitrile rubber | A piston gasket for low pressure | Since urethane rubber is used as gasket material, it has excellent wear resistance. |
| It can be used for both oil pressure and air pressure. | ||||
Gaskets for oil hydraulic cylinders (dedicated to rod seals)
| Shape classification | Cross-section shape of gaskets | Material | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
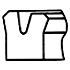
| L |
|
Urethane rubber, nitrile rubber, fluororubber | A gasket dedicated to rod seals. Gaskets made of urethane rubber have excellent wear resistance. | Excellent in sealing performance and durability. Gaskets with a small cross-sectional area can be mounted in integrated grooves. |
Gaskets for oil hydraulic cylinders (for pistons and rod seals)
| Shape classification | Cross-section shape of gaskets | Material | Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
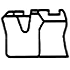
| U |
|
Urethane rubber | Can be used for both pistons and rod seals. Compared to dedicated gaskets, pressure resistance is slightly inferior. | Since urethane rubber is used as gasket material, they have high wear resistance, and gaskets with a small cross-sectional area can be mounted in integrated grooves. |
| Nitrile rubber | ||||
| Cold-resistant nitrile rubber | Since nitrile rubber,and cold-resistant nitrile rubber and fluororubber are used as gasket materials, they can be used at a wide range of temperatures or for ester phosphate hydraulic fluid. | |||
| Fluororubber | ||||
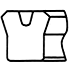
| V |
|
Cloth-inserted nitrile rubber | By using several gaskets in layers according to the working pressure, they can be used under harsh conditions. However, this type of gaskets has disadvantages, including inferior sealing performance, compared to U gaskets. | Equivalent to JIS B 2403. Cloth-inserted nitrile rubber is used as gasket material. For heat-resistant and chemical-resistant applications, cloth-inserted fluororubber is also used. |
| Cloth-inserted fluororubber | ||||

|
Nitrile rubber | Equivalent to JIS B 2403. Nitrile rubber is used as a gasket material. For heat-resistant and chemical-resistant applications, fluororubber is also used. | ||
| Fluororubber | ||||
Materials of lip gaskets and hydraulic fluids
To select a gasket material, suitability for the fluid to be sealed is important. The following table shows the suitability of materials for hydraulic fluids. Generally speaking, mineral hydraulic fluids are suitable for any materials for gaskets; however, when an extreme-pressure additive or other additive is contained for the purpose of improving oiliness, it is necessary to check for impact of the relevant additive on physical properties of rubber materials by performing rubber material testing.
Usable hydraulic fluids for gasket materials (former JIS B 8354)
| Hydrogenated NBR | Nitrile rubber | Urethane rubber | Fluororubber | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mineral | ○ | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Water-glycol | ○ | ○ | △ | △ |
| W/O emulsion | ○ | ○ | △ | ○ |
| O/W emulsion | ○ | ○ | △ | ○ |
| Ester phosphate | × | × | × | ○ |
| Fatty acid ester | △ | △ | △ | △ |
| Biodegradable | ○ | ○ | △ | △ |
| MIL-equivalent oil | △ | △ | ○ | ○ |
Selection of gaskets
The following table shows reference information for selection of gaskets. In the case of use of special fluids, or even under normal conditions of use, when (1) the relevant gasket is constantly subjected to the minimum working pressure of 3 MPa or more, or (2) the relevant gasket is used at a temperature and/or pressure close to the respective permissible levels, consult NOK.
Precautions of use of gaskets / opposite materials and finish methods
Except in special cases, use materials specified in former JIS B 8354 as an opposite material. Opposite sliding materials of gaskets and finish methods are described below.Conventionally, only finish roughness size has been discussed; however, roughness forms vary. Even if the size is within the range of the recommended values, in the case of waveforms with steep peaks, abnormal wear may occur. Use as reference “Definitions and indications of surface roughness” of JIS 0601-1994 revised in 1994, to which the load length rate tp, for quantitatively indicating the surface roughness form.
Opposite materials and finish methods
| Material | Finish method | |
|---|---|---|
| Cylinder tube | JIS G 3473 (Carbon steel pipes for cylinder tubes) | Honing or burnishing 0.4—3.2 μmRz (0.1—0.8 μmRa) |
| JIS G 3445 (Carbon steel pipes for mechanical structures) | ||
| Cylinder rod | JIS G 4051 (Carbon steel materials for mechanical structures) | After heat treating and polishing, hard chrome plating and buffing 0.8—1.6 μmRz (0.2—0.4 μmRa) |
Precautions of use of gaskets / plating
Hard chrome plating is quite commonly used for hydraulic cylinders. Its purposes include rust prevention and mechanical strength improvement. Hard chrome plating thickness is specified not according to the type of gaskets, but according to the use environment, use conditions, etc. in general. JOHS-110 “Japan Oil and Air Hydraulic Industrial Standards: hydraulic cylinders for iron-making machinery (heavy equipment)” specifies hard chrome plating thickness based on the types of hydraulic fluids shown as in the table below.
Hard chrome plating thickness (JOHS-110)
| Type of hydraulic fluid | Plating thickness (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| Tube inside surface | Rod surface | |
| Water-glycol fluid | 0.02 | 0.02 |
| General mineral hydraulic fluid | ||
| Phosphoester hydraulic fluid | ||
| W/O hydraulic fluid | ||
| O/W hydraulic fluid | 0.05 | 0.05 |
Precautions of use of gaskets / gaps due to protrusion and bearing gaps
Gaps due to protrusion and bearing gaps regarding gaskets are closely related to performance of the gaskets. It is preferable to make bearing gaps as small as possible without compromising performance of the hydraulic equipment. Regarding gaps due to protrusion, a limit diagram for protrusion of seal materials is shown in the following table as reference.
Back-up rings
To prevent gaskets from protruding, it is common that gaskets are used in combination with synthetic-resin back-up rings. For use of back-up rings, take note of the following description. (1) Since dimensions of polyamide resin change due to absorption of water and drying, in the case of a large-diameter back-up ring, a bias cut should be provided for the sake of improving mountability. In the case of an endless back-up ring, to suppress permeation of moisture, a change in dimensions due to absorption is prevented by including a desiccant in the special package. (2) Both gaskets and back-up rings deform due to pressurization, and the deformation amount and deformation rate differ according to materials of the gaskets and back-up rings. If the deformation rate of the gasket and back-up ring is different significantly, the back-up ring’s intended purpose of protecting the gasket cannot be accomplished. Therefore, soft rubber materials for gaskets (nitrile rubber, fluororubber) should be combined with soft resin materials for back-up rings (PTFE), and in the case of use in a high-pressure area, a combined use of PTFE with polyamide resin, which is a harder material for back-up rings, is desirable.
Example of use of gaskets (U-gaskets)
The following figure shows mounting groove dimension tolerances and finish examples of representative U-gaskets.
Example of use of gaskets (combination gaskets)
The following figure shows mounting groove dimension tolerances and finish examples of combination gaskets.